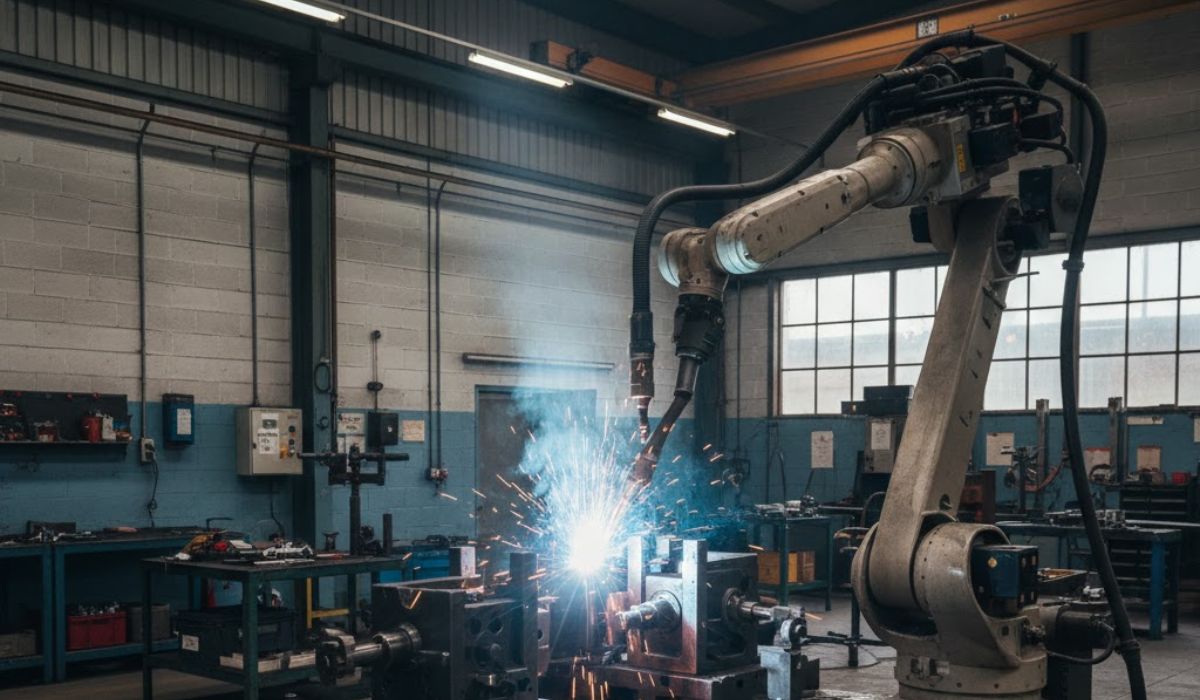
As manufacturing shifts toward automation, robotic welding systems are increasingly used across automotive, fabrication, and heavy engineering sectors. While robots receive most of the attention, the accuracy and repeatability of any automated welding process depend heavily on the fixturing used to hold and locate parts during welding.
This article explains how automated welding fixtures work, why their design matters, and how proper fixturing directly impacts weld quality and production stability.
What Is a Welding Fixture in Robotic Automation?
In an automated welding setup, fixtures are used to position, support, and secure components so that the welding robot can follow a programmed path without variation.
Unlike manual setups, automated welding relies on consistent part positioning, not operator adjustment. Even small shifts in component location can result in misaligned welds or inconsistent penetration.
Why Accurate Fixturing Is Essential in Robot-Based Welding
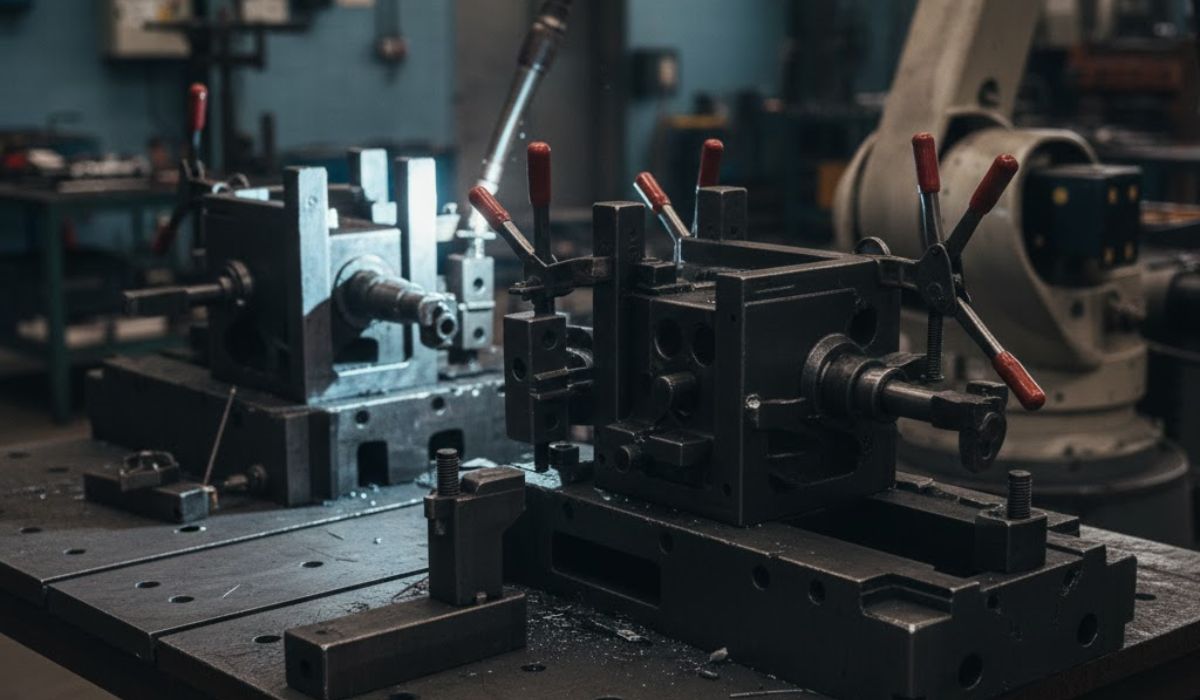
Robots repeat the same motion cycle every time. If a part is not placed correctly, the robot will not compensate.
Proper fixturing helps by:
-
Maintaining stable joint location
-
Preventing movement during welding
-
Supporting repeatable cycle times
-
Reducing dependency on operator skill
In automated environments, fixturing accuracy is often more critical than robot precision.
Manual vs Automated Welding Fixtures
Many production issues occur when fixtures designed for manual welding are reused in automated cells.
Key differences include:
-
Higher positional accuracy requirements
-
Use of pneumatic or hydraulic clamping
-
Consideration of torch access angles
-
Design for high-volume repetition
Fixtures that work well for manual operations often fail when exposed to automated cycle speeds.
Common Fixturing Approaches Used in Automated Welding
Pneumatically Actuated Fixtures
These systems use air-driven clamps to provide consistent and repeatable clamping force. They are commonly applied in automated welding cells where fast cycle times are required.
Modular Fixturing Systems
Modular setups use standard elements that can be rearranged. They are suitable for low to medium production volumes, prototypes, or flexible manufacturing environments.
Dedicated Automation Fixtures
Custom-built fixtures designed for a specific component offer maximum rigidity and accuracy. These are typically used in high-volume production lines where repeatability is critical.
Key Design Considerations for Automated Welding Fixtures
Effective fixture design focuses on stability and simplicity rather than complexity.
Important aspects include:
-
Proper locating strategy based on the 3-2-1 principle
-
Controlled clamping to avoid part distortion
-
Unobstructed access for the welding torch
-
Rigid base construction to resist vibration
-
Ease of part loading and unloading
Neglecting these fundamentals often leads to quality and maintenance issues.
Repeatability: The Core Requirement in Automated Welding
In automated welding, repeatability matters more than absolute accuracy.
Fixtures must:
-
Hold every component in the same position
-
Maintain geometry over extended production runs
-
Resist wear at locating and clamping points
Loss of repeatability leads to inconsistent welds and increased rework.
Problems Caused by Poor Fixturing in Automation
When fixtures are poorly designed or inadequately maintained, manufacturers commonly face:
-
Irregular weld bead appearance
-
Frequent program adjustments
-
Higher rejection rates
-
Increased downtime
-
Reduced equipment life
These issues are often incorrectly attributed to robots or welding parameters rather than fixturing.
Integration of Fixtures in Automated Production Lines
In fully automated environments, welding fixtures often operate alongside:
-
Conveyors
-
Positioners
-
Turntables
-
Sensors and safety interlocks
This requires fixtures to be designed as part of the overall automation system, not as isolated tools.
Final Thoughts
In automated welding applications, fixtures play a critical role in ensuring consistency, efficiency, and quality. While robots execute the weld, it is the fixturing system that determines whether the process remains stable over time.
Understanding how automated welding fixtures function and why thoughtful design matters helps manufacturers achieve reliable outcomes in robot-based welding operations.
FAQs – Automated & Robotic Welding Fixturing
Q1. Why is fixturing so important in automated welding?
In automated welding, the robot follows a fixed programmed path. Accurate fixturing ensures that every part is held in the same position, which is essential for consistent weld quality and repeatability.
Q2. Can fixtures designed for manual welding be used in robotic welding?
Usually no. Manual welding fixtures lack the rigidity, positional accuracy, and repeatability required for automated welding systems, which often leads to weld defects and frequent adjustments.
Q3. What is the main difference between modular and dedicated fixtures?
Modular fixtures offer flexibility and are suitable for low to medium production volumes, while dedicated fixtures are custom-built for specific parts and provide higher accuracy and stability for high-volume automated production.
Q4. How does poor fixture design affect weld quality?
Poor fixturing can cause part movement, inconsistent joint positioning, and vibration during welding. This often results in uneven weld beads, rework, and reduced production efficiency.
Q5. What role does repeatability play in automated welding fixtures?
Repeatability ensures that every component is positioned exactly the same way in each cycle. In automated welding, consistent positioning is more critical than absolute accuracy.
Q6. Do automated welding fixtures need regular maintenance?
Yes. Locating points, clamps, and moving elements experience wear over time. Regular inspection and maintenance help maintain accuracy and long-term process stability.
Q7. How are fixtures integrated into automated welding lines?
In automated lines, fixtures are often integrated with positioners, conveyors, turntables, and safety systems. This allows smooth part handling and uninterrupted welding cycles.

